Discover how Sky-Walker GIS integration improves the efficiency of your control room
What are GIS integrations?
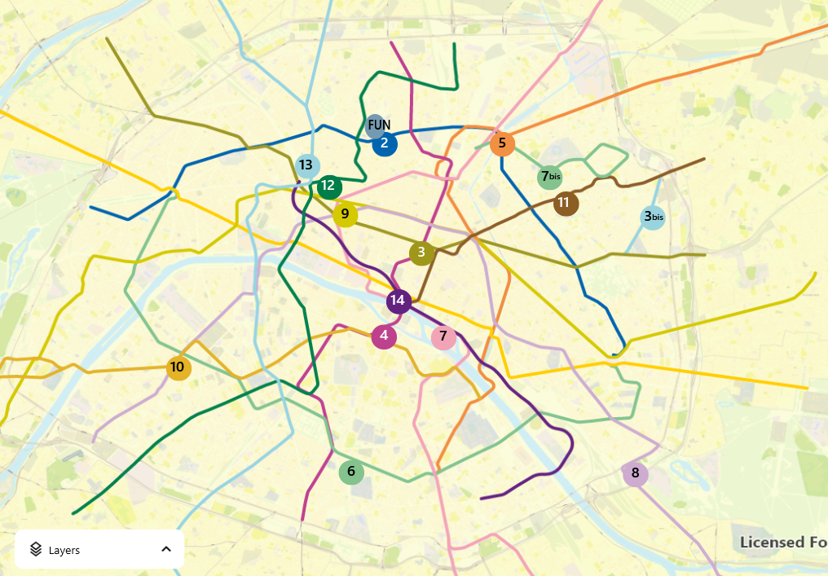
GIS provides a powerful framework for integrating diverse datasets and visualizing them on a map, making complex spatial relationships easier to understand. By layering data such as population density, infrastructure, environmental information, and customer locations, organizations are better equipped to make informed decisions. This is especially useful for planning facilities, optimizing emergency routes, analyzing urban growth, and managing resources effectively.
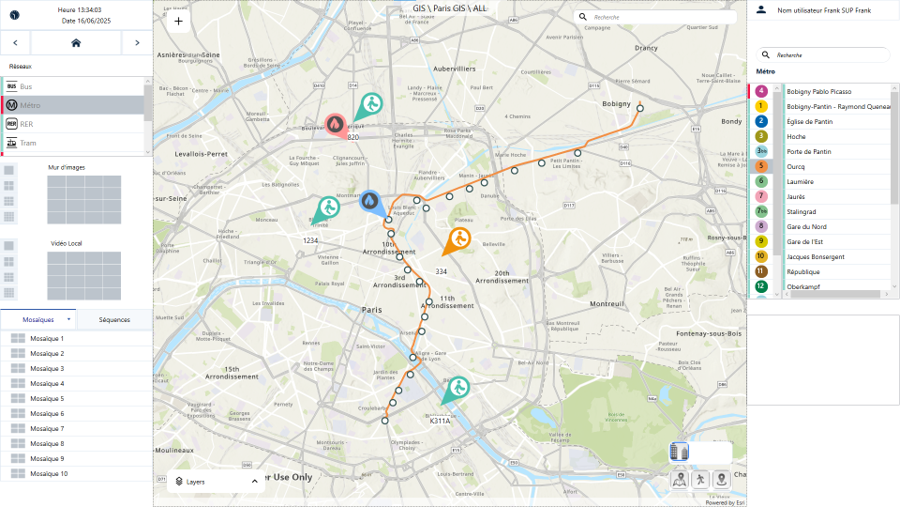
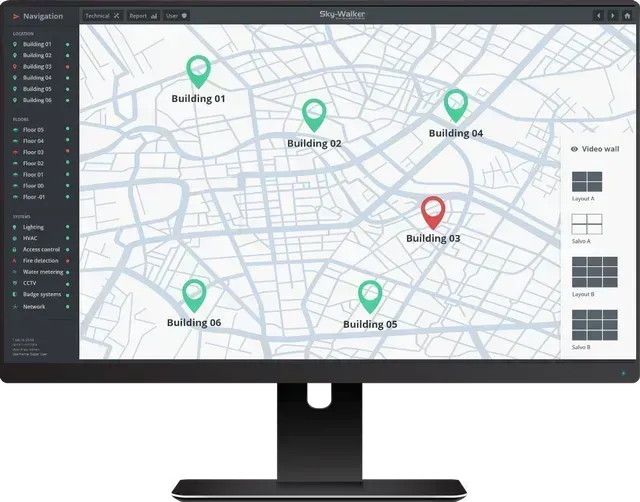
We understand that real-time insights are key to maintaining efficient control rooms. That’s why our Sky-Walker GIS integration takes this a step further by offering spatial data visualized on interactive maps. Whether managing multiple teams across locations or coordinating simultaneous incidents, our solution brings clarity and control right to the operator’s workstation.

What Can You Expect from Sky-Walker GIS Integration?
When an alarm is triggered, the incident location appears immediately on-screen and is updated in real time. This live mapping helps operators track the situation’s progress and coordinate mobile teams more easily, saving time and resources.
Key features:
🔄 Real-time location updates of incidents and mobile teams
🗺️ Interactive maps with customizable layers
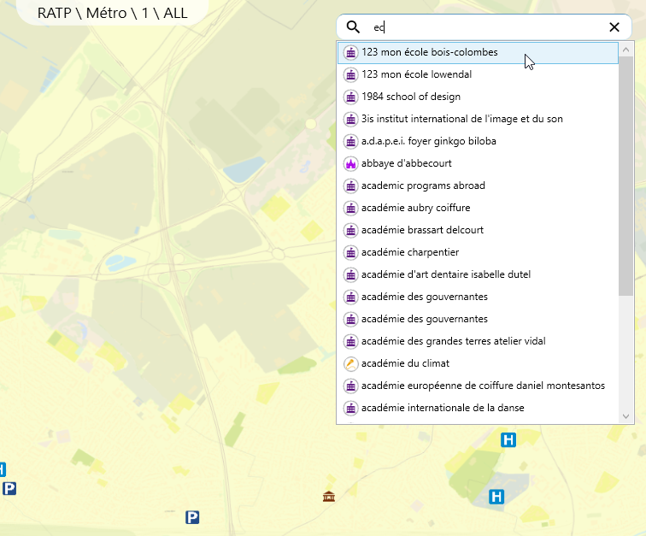
🌐 Integrated search and geocoding functionality
🔎 Dynamic zoom ranges for detail and wide-area visibility
📍 Markers to highlighting key points or threats
What GIS features does Sky-Walker have?
Map & Layers
Visualize complex spatial data through customizable layers to get a clear overview of your operational area.
Search function
Quickly find locations and incidents with a search tool integrated into the system.
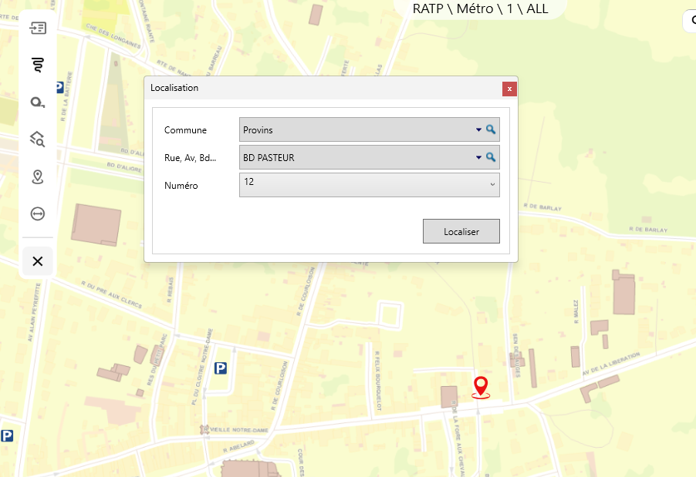
Geocoding
Convert addresses or place names into geographic coordinates to pinpoint incident locations precisely.
Zoom ranges
Zoom in and out to focus on details or get a broader view of the area.
Mobile teams
Track your mobile teams live on the map to optimize response and coordination.
Marker
Use markers to highlight important locations or incidents for quick reference.
7 key advantages of using GIS integration
1. Intuitive handling of alarms
2. Real-time traffic information
3. Fully modular and customizable
4. Better overview of multiple incidents
5. Easily manage mobile teams
6. Real-time status updates
7. Platform independent
8. Efficiency in emergencies
Key Components of GIS
Spatial Data
Also known as geospatial data, this refers to information connected to the location and shape of objects like roads, rivers, and buildings. The data comes in two main formats: vector and raster. Spatial data is integrated and uses shared coordinate systems. This integration makes it easier to analyse and help with location-based decisions.
Attribute Data
It provides detailed information about the spatial features, such as population density and land use. These features are stored in databases and can be linked to spatial data through unique identifiers like country codes. By connecting the attribute data to the geographic features, we enable deeper analysis and clearer visualization.
GIS Software
The GIS software is designed to combine geographic data with other types of information to create maps, analyze spatial patterns, and support better decision-making. Tools like
ArcGIS, QGIS, and
Google Earth help streamline the process, explore geospatial data, and make complex spatial information easier to use.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing involves collecting data by using satellites or aerial imagery. This data is then integrated into the GIS platforms, where it's organized and visualized. Remote sensing and GIS allow useful applications in areas like environmental monitoring, disaster response, and resource management.
7 Significant benefits of GIS
1. Enhanced Decision-Making and Planning
GIS combines multiple data sources into one clear map view. By layering information such as population density, infrastructure, and risk zones, organizations gain better insight into complex situations. This visual clarity supports strategic planning and more informed decision-making.
2. Improved Communication and Collaboration
Maps are highly effective tools for communication. GIS takes it further by transforming complex data into interactive visuals that are easy to understand. This enhances teamwork and ensures that all stakeholders share a common understanding of the situation.
3. Optimized Resource Management
GIS helps organizations manage resources effectively. Utility companies use it to map infrastructure and schedule maintenance, while agricultural teams combine weather patterns with land data to optimize crop yield and water usage, resulting in smarter planning and reduced waste.
4. Better Asset Management and Maintenance
GIS provides a structured, map-based system to track, manage, and maintain assets like streetlights and fire hydrants to schedule repairs. Telecommunications companies use GIS to oversee network infrastructure, quickly detecting areas that need upgrades. This results in cost savings and reduced time.
5. Environmental Protection and Conservation
GIS helps urban planners understand and protect natural ecosystems. It’s used to track deforestation and model flood risks. By combining satellite imagery with on-the-ground data, GIS enables detailed environmental analysis, guiding sustainable decision-making.
6. Enhanced Public Safety and Emergency Response
Emergency services use GIS to plan patrols, respond to incidents, and manage disasters. GIS plans evacuations and identifies impacted zones during floods and earthquakes, saving time and lives.
7. Market Analysis and Business Development
Businesses use GIS to get insights into market trends and customer behavior. GIS assists retailers in evaluating traffic flow and competitor locations to choose the best spots for new stores. Marketing teams improve campaigns by knowing where their audiences are located, and real estate developers assess property values.








 Download Product Ebook
Download Product Ebook View all our solutions
View all our solutions Sky-Walker Architecture
Sky-Walker Architecture View all our integrations
View all our integrations Book Protocol workshop
Book Protocol workshop Our Company
Our Company Contact Us
Contact Us View All Our Case Studies
View All Our Case Studies Become a PSIM Partner
Become a PSIM Partner Become a Sky-Walker PSIM partner today!
Become a Sky-Walker PSIM partner today! English
English Français
Français Nederlands
Nederlands